In today’s modern world, where almost every device depends on electricity, voltage transformers play a vital role in keeping our equipment safe and functional. Whether it’s your phone charger, television, or large industrial machine, a transformer ensures that each device receives the right amount of voltage to work efficiently.
If you’ve ever wondered what exactly a transformer does, how it works, and why it’s important, this complete beginner’s guide is for you.
What Is a Voltage Transformer?
A voltage transformer is an electrical device that changes (or “transforms”) the voltage level of an alternating current (AC) from one level to another — either higher or lower.
In simple terms:
- Step-up transformer increases voltage.
- Step-down transformer decreases voltage.
Transformers are used everywhere — from power stations that generate electricity to the small chargers that power your gadgets. They make sure that the electricity supplied is at a safe and usable voltage for your devices.
🔹 Why Do We Need Voltage Transformers?
Electricity generated at power plants travels long distances before reaching your home or office. During this journey, voltage levels need to be adjusted for efficiency and safety.
Here’s why transformers are essential:
- Efficient Power Transmission
High voltage means less energy loss during transmission. Step-up transformers raise voltage levels to send electricity over long distances. - Safe Power for Devices
The electricity that enters your home must be safe for everyday appliances. Step-down transformers reduce the voltage to a usable level (e.g., from 11,000V to 230V). - Protection from Damage
Without transformers, many electrical devices would burn out or fail due to voltage fluctuations. - Compatibility Across Regions
Different countries use different voltages (e.g., 110V in the US, 230V in India). Step-up or step-down transformers make it possible to use foreign appliances safely.
🔹 The Basic Working Principle of a Transformer
The transformer works on a simple yet powerful principle of electromagnetic induction — discovered by Michael Faraday.
Let’s break it down step by step:
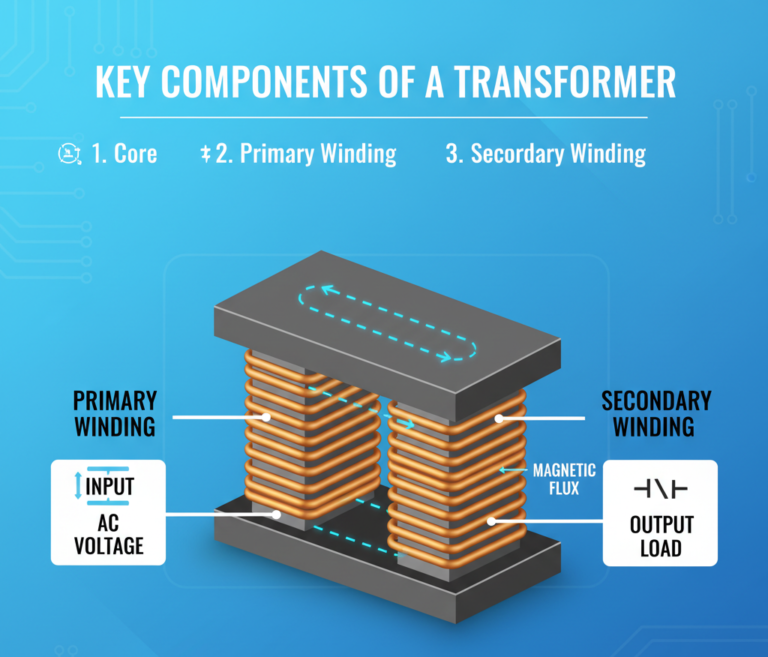
- Two Coils, One Core
A transformer has two sets of coils — the primary coil and the secondary coil — wound around a common iron core. - AC Current in the Primary Coil
When alternating current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field around it. - Induced Voltage in the Secondary Coil
This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil — this process is known as mutual induction. - Voltage Transformation
The ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coils determines whether the voltage is increased or decreased.
The formula is simple:
V₁ / V₂ = N₁ / N₂
- V₁ = Primary voltage
- V₂ = Secondary voltage
- N₁ = Number of turns in primary coil
- N₂ = Number of turns in secondary coil
- If N₂ > N₁ → Step-up transformer
- If N₂ < N₁ → Step-down transformer
🔹 Types of Voltage Transformers
Transformers come in different sizes and types, depending on their use. Here are the most common ones:
1. Step-Up Transformer
- Increases voltage from a lower level to a higher level.
- Commonly used in power plants and transmission systems.
- Example: Converts 11kV to 220kV for efficient transmission.
2. Step-Down Transformer
- Reduces voltage to a safer, lower level for homes and offices.
- Example: Converts 220V to 12V or 24V for low-voltage electronics.
3. Isolation Transformer
- Used for safety and protection by isolating two circuits.
- Helps prevent electrical shocks and interference.
4. Autotransformer
- Uses a single winding for both primary and secondary functions.
- Compact, efficient, and often used in variable voltage equipment.
5. Instrument Transformers
- Includes Potential Transformers (PT) and Current Transformers (CT), used in measurement and protection systems.
🔹 Applications of Voltage Transformers
Transformers are everywhere — from massive power grids to tiny electronic devices. Here are a few real-world applications:
- Power Distribution Networks
Transformers help deliver electricity safely from power stations to homes, offices, and factories. - Electronics and Appliances
Your phone charger, TV, and audio system all use small step-down transformers to reduce voltage safely. - Industrial Machines
Factories use heavy-duty transformers for large motors, welding machines, and automation equipment. - Renewable Energy Systems
In solar and wind setups, transformers regulate and match voltages before feeding power to the grid. - Travel and International Use
Step-up/step-down travel transformers allow you to use gadgets in countries with different voltage standards.
🔹 How to Choose the Right Transformer
Choosing the correct transformer depends on your needs. Here’s what to consider:
- Input and Output Voltage
Know the voltage you have and the voltage your device needs (e.g., 220V to 110V). - Power Rating (Watts or VA)
Check your device’s wattage and choose a transformer rated 20–30% higher for safety. - Type of Load
- Resistive loads: lamps, heaters, toasters
- Inductive loads: motors, compressors, fans (require higher capacity)
- Frequency Compatibility
Make sure the transformer supports your region’s frequency (50Hz or 60Hz). - Quality and Safety Certification
Look for ISO, CE, or RoHS certifications to ensure reliability and safety.
🔹 Safety Tips When Using Transformers
Even though transformers are designed for protection, mishandling can be dangerous. Keep these safety tips in mind:
- Always use a transformer with the correct voltage rating.
- Avoid overloading the transformer.
- Keep it in a dry, well-ventilated area.
- Do not cover or block the air vents.
- Regularly inspect for overheating or unusual noise.
🔹 Common Myths About Transformers
Let’s clear up some misconceptions:
- Myth 1: Transformers work with DC power.
Fact: Transformers only work with alternating current (AC). - Myth 2: Bigger transformers are always better.
Fact: Using an oversized transformer wastes energy and money. - Myth 3: All adapters are transformers.
Fact: Adapters may contain transformers, but not all adapters perform voltage transformation.
🔹 The Future of Transformers
With the rise of renewable energy and smart grids, transformer technology is evolving.
Modern transformers are becoming:
- Smaller and more efficient
- Eco-friendly (using biodegradable insulation oils)
- Smart (with sensors for real-time monitoring and performance tracking)
As electricity demands continue to grow, transformers will remain a key component of our energy infrastructure — ensuring power is always delivered safely and efficiently.
🔹 Final Thoughts
Understanding how voltage transformers work helps you make smarter decisions when buying or using electrical devices.
They might seem complex, but their function is simple: to keep your electronics running safely and efficiently by delivering the right voltage at the right time.
Whether it’s a small adapter for your phone or a massive industrial transformer, these devices silently power our daily lives — making modern living possible.





